The future of Robotic Process Automation(RPA) looks bright as experts project the market to exceed $5 billion by 2025. The market has matured naturally with growth rates changing from 63% in 2020 to 22% in 2022. This reflects market stability rather than slower adoption.
The possibilities expand when RPA is combined with artificial intelligence. Hyperautomation’s market value stands at $12.95 billion today and could reach $31.95 billion by 2029. The numbers tell an interesting story – only 10% of people interact with smart robots now, but this number could jump to 80% by 2030.
This piece takes you through RPA’s changing digital world and what to expect in 2025 and beyond. You’ll find how cloud-based solutions and AI integration are altering the map of business automation.
What Is RPA And Why Is it Gaining Attention?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is drawing interest as it improves efficiency, lowers expenses, and lessens human mistakes. Automating tedious processes helps companies to release workers for more valuable employment. Artificial intelligence and machine learning together let RPA manage complicated operations, hence enhancing decision-making and client interactions. Low-code systems and cloud-based RPA let businesses of all sizes automate.
RPA also provides a good return on investment by lowering costs by as much as 50%. RPA is essential in maximizing operations, guaranteeing scalability, and keeping security standards compliance as companies give digital transformation top priority.
Is RPA Still Relevant in 2025?
Despite predictions that more advanced technologies would make RPA obsolete, it remains not only relevant but increasingly critical to organizational operations in 2025. Several factors contribute to RPA’s enduring relevance:
First, the proliferation of applications and systems in most organizations has created an integration challenge that API-based approaches cannot fully address. The average enterprise uses over 500 applications, with many legacy systems lacking modern integration capabilities. RPA fills this integration gap without requiring costly system replacements or extensive custom development.
Second, RPA has evolved significantly from its initial capabilities. Modern RPA platforms incorporate AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, addressing many of the limitations of early RPA tools. This evolution has enabled RPA to handle increasingly complex processes that require judgment, adaptation, and learning—capabilities once thought to be beyond the scope of RPA.
Third, the economic imperative for automation continues to grow. With 45% of business tasks considered automatable, organizations face increasing pressure to improve productivity and reduce costs. RPA delivers rapid ROI—typically 30-200% in the first year—making it an attractive investment compared to many other digital transformation initiatives.
Lastly, the human element cannot be overlooked. As organizations implement automation, they’re discovering that the optimal approach often combines human and digital workers. RPA’s ability to work alongside humans, handling repetitive tasks while humans focus on exception handling and creative problem-solving, creates a collaborative model that maximizes the strengths of both.
Will RPA become obsolete?
The question of RPA’s obsolescence is complex. While the core concept of UI-based automation will likely remain relevant, the form and capabilities of RPA will continue to evolve. Several trends suggest that RPA will not become obsolete but rather transform into something more capable:
The integration of AI technologies is transforming RPA from a deterministic tool into an adaptive automation platform. As one expert aptly stated, “RPA is our hands, while AI is our brain”. This combination creates intelligent automation that can handle exceptions, learn from experience, and make context-aware decisions—addressing the primary limitations of traditional RPA.
The emergence of AI Agents represents the next evolutionary step for RPA. These agents combine large language models with RPA’s execution capabilities, creating systems that can understand natural language instructions, plan complex sequences of actions, and dynamically adapt to changing conditions. For example, Tsinghua University’s ProAgent can autonomously build workflows and make dynamic decisions based on business scenarios.
Moreover, as organizations progress in their automation journeys, they’re developing hybrid approaches that combine API-based integration with UI-based automation where appropriate. This pragmatic approach recognizes that different integration methods have different strengths and trade-offs, with RPA filling specific gaps where other methods are impractical or cost-prohibitive.
While specific RPA tools may become obsolete as technology advances, the fundamental need for cross-application automation will persist. The convergence of RPA with adjacent technologies suggests that rather than disappearing, RPA will become embedded within broader intelligent automation platforms that offer multiple integration modalities.
Where does RPA fit with other automation technologies?
Robotic Process Automation occupies a unique position in the automation technology landscape. Unlike traditional automation approaches that require deep system integration and API access, RPA operates at the presentation layer, mimicking human interactions with digital systems. This characteristic allows RPA to complement rather than compete with other automation technologies.
RPA serves as a connective tissue between disparate systems that lack native integration capabilities. While technologies like API-based integration provide deeper and more robust connections, RPA offers agility and rapid implementation. For organizations with legacy systems that don’t expose APIs or have complex custom interfaces, RPA becomes the only viable automation solution without undertaking costly system modernization projects.
The emergence of hyperautomation—the combination of RPA with AI, process mining, analytics, and other advanced tools—has positioned RPA as the execution layer within a broader automation ecosystem. Process mining tools identify automation opportunities and process inefficiencies, AI/ML components handle cognitive tasks like document analysis and prediction, while RPA robots execute the actual workflow steps across applications. This synergistic relationship allows organizations to achieve end-to-end automation that would be impossible with any single technology alone.
How does generative AI fit in?
Generative AI has dramatically expanded the capabilities of RPA, transforming it from a rules-based automation tool into a cognitive automation platform. The integration of generative AI with RPA is arguably the most significant development in the automation landscape in 2025, with 90% of RPA providers offering generative AI-assisted automation capabilities.
One of the most impactful applications of generative AI in RPA is in the development process itself. Natural language interfaces allow developers to describe processes in plain English rather than coding them manually. For instance, Octoparse AI’s Copilot functionality claims to improve development efficiency through natural language process creation. This democratization of development enables business users with domain expertise but limited technical skills to create and modify automation workflows.
Generative AI also enhances RPA’s ability to handle unstructured data. Traditional RPA struggled with documents that didn’t follow strict templates, but AI-powered document processing can now understand, categorize, and extract information from varied documents like invoices, contracts, and emails with human-like comprehension. One financial institution reported achieving 98% accuracy in contract review after integrating generative AI with their RPA system.
Furthermore, generative AI enables predictive automation, where systems can anticipate next steps based on historical patterns and current context. This shift from reactive to proactive automation represents a fundamental change in how organizations approach process automation, potentially delivering value beyond mere efficiency gains.
Which Industries will Take Advantage of This Tech?
Virtually every industry stands to benefit from RPA and intelligent automation, but some sectors are further advanced in their adoption and realizing greater benefits:
- Financial Services: The finance industry remains at the forefront of RPA adoption, with 65% of finance firms planning to increase automation investment. Banks and insurance companies use RPA for processes like claims processing (75% faster than humans), fraud detection, compliance reporting, and customer onboarding. The highly rule-based nature of many financial processes makes them ideal for automation.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations are using RPA to address administrative burdens that divert resources from patient care. Applications include patient scheduling, insurance verification (90% reduction in processing time), claims processing, and data migration between systems. The potential annual savings of $17.6 billion for the healthcare industry demonstrates the significant impact of automation in this sector.
- Manufacturing: While slower to adopt RPA than some industries, manufacturing has seen rapid recent growth with 43% of manufacturers now using RPA. Use cases include supply chain coordination, order processing, inventory management, and ERP data maintenance. The integration of RPA with IoT devices is particularly promising for predictive maintenance and quality control.
- Government: Public sector organizations use RPA to improve service delivery while constrained by limited budgets. Applications include citizen record management, benefit eligibility verification, tax processing, and regulatory compliance. The highly standardized processes and need for audit trails in government work align well with RPA’s strengths.
- Retail and Logistics: These industries leverage RPA for supply chain optimization, inventory management, customer service, and order processing. The e-commerce sector particularly benefits from automation, with logistics companies reporting significantly higher profit margins ($12-20 per $100 in e-commerce sales) due to automation.
What distinguishes leading organizations in these industries is not merely implementing RPA, but building an automation-first culture that continuously identifies and prioritizes automation opportunities. These organizations are also moving beyond isolated automation projects to develop enterprise-wide automation strategies that maximize value across the organization.
What Are the Trends for RPA in 2025?
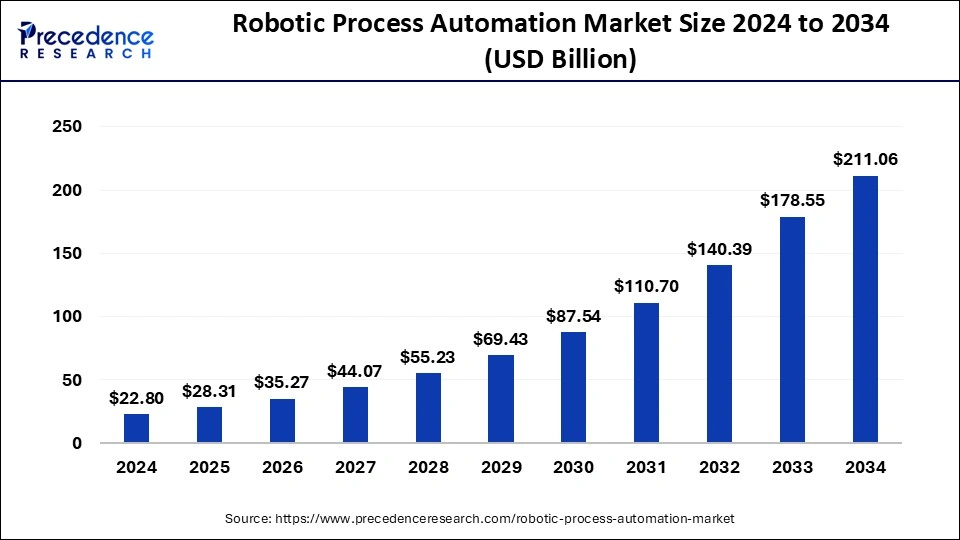
RPA market projections show huge growth potential for 2025. Financial forecasts predict the global RPA market will reach anywhere from USD 28.31 billion to USD 40.56 billion by 2025. The market could climb to USD 211.06 billion by 2034. These numbers show a compound annual growth rate between 25.01% and 43.9%, based on different analysis methods.
North America leads the RPA market with 38.92% of the global market share. The Asia Pacific region will grow the fastest through 2025 at a CAGR of over 46%. This change comes from higher RPA adoption in pharmaceutical, healthcare, IT, telecom, retail, and manufacturing sectors across Asia.
The industry-specific use of RPA will keep growing in 2025. Healthcare shows strong momentum because automation brings clear improvements in medical records management, order entry, and decision support. These changes lead to fewer patient complications and lower costs. Banks and financial firms are pushing for automation too, with 65% of organizations planning big investments in financial process automation.
The biggest tech change by 2025 will be how generative AI works with RPA. Gartner says 90% of RPA vendors will offer generative AI-assisted automation. This combination will change how businesses handle complex decisions and solve the limits of traditional RPA systems.
The numbers behind these predictions look promising. Studies show that 79% of RPA projects save time, 69% boost productivity, and 61% cut costs. Companies looking to improve operations see RPA as a one-time investment that can bring big returns.
The Business Process Outsourcing sector offers a major growth area for RPA in 2025. The technology helps optimize workflows, makes work more accurate, and lets companies scale up easily.
RPA evolves faster than simple task automation in 2025. Several trends reshape its role across industries.
AI integration with RPA leads innovation today. Gartner predicts 90% of RPA vendors will offer generative AI-assisted automation to improve customer experiences by 2025. This powerful combination helps bots process unstructured data, understand natural language, and make real-time decisions that reshape automation capabilities.
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation emerges as another most important trend that combines RPA with AI, machine learning, and process mining.
Cloud-based RPA
Cloud-based RPA is gaining momentum and provides organizations with a unified platform for automation services. Thanks to improved scalability and accessibility, organizations can deploy automation solutions without large infrastructure investments.
RPA Democratization
RPA democratization through low-code and no-code platforms extends automation capabilities to non-technical users. Small and medium enterprises can now utilize automation without specialized IT resources. This promotes innovation in organizations of all sizes.
Security and Governance
Security and governance focus intensifies as automation adoption grows. Organizations prioritize secure RPA implementations with resilient cybersecurity measures. This approach ensures automation expansion maintains data integrity and compliance.
These developments show RPA’s future goes nowhere near simple task automation. It becomes crucial to detailed digital transformation strategies.
Frequently Recommended RPA Tool: Octoparse AI
The market is flooded with RPA software options, each tailored for specific user types and business needs. Here I recommend Octoparse AI—a free RPA tool that lets you experience all essential RPA functionalities without any cost. You can also try its team collaboration features through a free trial.
Octoparse AI is perfect for e-commerce, marketing, and research teams looking to automate data collection without technical expertise, thanks to its no-code visual interface and AI-powered adaptability.
It offers a free plan with basic workflow, making it accessible for even the smallest businesses. Alternatively, you can opt for the starter plan at $29/month or the Team plan at $49/month (billed annually). Enterprise pricing is also available with custom solutions and dedicated support.
Key Strengths:
- Easily extracts data from complex websites
- Handles dynamic content & unstructured data
- User-friendly visual interface (no coding needed)
- AI automatically adjusts to website changes
Final Thoughts
RPA has reached a turning point that will change business operations through 2025 and beyond. Market projections support this view, as the market will grow to $40.56 billion by 2025 and reach an impressive $211.06 billion by 2034.
RPA and artificial intelligence meet through generative AI capabilities. This represents progress from simple automation to intelligent process optimization. The rise of hyper-automation helps organizations handle complex processes while cutting costs by 25% to 50%.
Growth patterns look promising in the Asia Pacific region where companies adopt RPA at increasing rates. Healthcare, financial services, and business process outsourcing lead to these changes. This shows RPA’s ability to work in different industries.
Cloud-based and low-code solutions make RPA available to businesses of all sizes. Companies can expect first-year ROI rates between 30% and 200%, which makes RPA a smart investment for better operations.
RPA’s future goes beyond simple task automation. It has become a key part of detailed digital transformation strategies. Companies that adopt these technological advances now will compete better in our increasingly automated business world.
